TL;DR
TNF inhibitors, the original workhorses of immunology & inflammation (I&I), dominated for two decades but face declining relevance due to non-response, safety concerns, and biosimilar competition. The field is now shifting toward IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors, which offer greater specificity, better durability, and cleaner safety profiles, particularly in psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. While TNF saw a temporary spike in 2022 due to COVID-related trial delays, repurposing, and biosimilars, the long-term trend favors more selective targets. Emerging I&I strategies also involve B cell (CD19/20) and JAK pathways, though JAK inhibitors face safety scrutiny. Staying ahead requires tracking mechanistic transitions, competitive shifts, and development patterns, ensuring strategic decisions and BD opportunities align with evolving therapeutic landscapes.
TNF: The Original Workhorse of I&I
The approval of infliximab in 1998 marked the beginning of targeted cytokine therapy in I&I — moving the field beyond steroids and broad immunosuppressants. Over the next two decades, Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) inhibitors like infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab became foundational treatments across rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, IBD, and more.
Their dominance was built on TNF’s central role in inflammation, rapid symptom relief, and early market entry. But over time, challenges emerged: non-response in some patients, loss of efficacy in others, and increased infection risk. As biosimilars diluted commercial returns and safety concerns grew, attention shifted toward more selective, better-tolerated targets — marking the slow but steady decline of TNF as the field’s anchor mechanism.
A New Axis of Activity: The IL-17/23 Era
By the mid-2010s, Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and Interleukin-23 (IL-23) began to gain traction as next-generation targets, offering greater specificity and potentially fewer off-target effects. What began as a supplemental strategy has now matured into a strategic pivot. In diseases like psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis, IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors have demonstrated robust, often superior outcomes relative to TNF blockers — with cleaner safety profiles and longer response durability.
These targets are biologically adjacent: IL-23 sits upstream of IL-17 in the inflammatory cascade. While IL-17 inhibitors (like secukinumab and ixekizumab) block the effector cytokine directly, IL-23 inhibitors (such as guselkumab and risankizumab) suppress its activation pathway. This mechanistic relationship has allowed for overlapping — but distinct — clinical strategies, and given developers multiple entry points across indications.
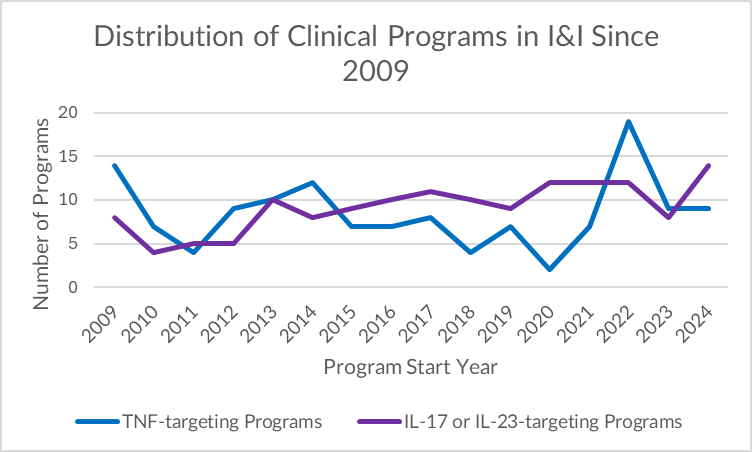
The 2021 Spike: A Curious Return for TNF
An unexpected spike in TNF-related clinical programs appears in 2022, disrupting an otherwise steady decline. This sudden resurgence does not reflect renewed long-term interest in the mechanism — instead, several plausible hypotheses could explain the deviation:
- Post-COVID backlog: Trials paused or delayed during the pandemic may have been reactivated or initiated in 2022, creating a temporary inflation in program starts.
- Repurposing efforts: There may have been short-term repositioning efforts of TNF inhibitors for immune-mediated complications or post-viral syndromes — strategies that did not carry into 2023.
- Biosimilar momentum: A wave of biosimilar development or expansion into new geographies may have artificially inflated trial counts, especially among late-phase or regional programs.
Whatever the cause, the spike appears to be an anomaly. TNF-related activity resumed its downward trajectory in 2023 — reinforcing the broader industry transition toward more differentiated cytokine targets.
Why the Handoff Matters
This shift isn’t just about a changing trend — it marks a fundamental realignment in how immunological diseases are being understood and treated. TNF inhibitors helped define the biologic era in I&I, but the rise of IL-17 and IL-23 reflects a more selective, mechanism-driven approach to immune modulation. These newer targets don’t just offer novelty — they offer precision, better durability, and often cleaner safety profiles, especially in dermatologic and spondyloarthritic indications.
For developers, this handoff means that:
- New TNF programs face structural headwinds: Unless highly differentiated or biosimilar-focused, they risk being clinically redundant or commercially boxed out.
- IL-17/IL-23 have momentum and regulatory familiarity: The path to market is clearer, but competition is tightening — particularly in psoriasis and PsA.
- The bar for new entrants is rising: Success will depend on pinpointing underserved indications, co-formulation strategies, or novel delivery platforms.
Beyond Cytokines: JAK, CD19/20, and the B Cell Play
While IL-17 and IL-23 dominate today’s momentum, other immune targets remain active — though they follow different storylines:
- CD19 and CD20 have drawn significant investment in lupus and RA, with B cell depletion strategies carving out space particularly in severe, refractory cases. These targets represent a more specific subset of I&I development and are not part of the broader cytokine-shifting trend this analysis focuses on.
- JAK inhibitors, once seen as a major leap forward, have faced mounting regulatory scrutiny over safety. As covered in a prior insight drop, the class saw a clear decline in clinical program initiations after 2021, driven by FDA warnings around cardiovascular and malignancy risk.
- IL-4/IL-13, particularly via dupilumab, continue to define therapeutic standards in atopic dermatitis and related Type 2-driven diseases, but their expansion beyond allergic pathways remains limited.
How We Support Decision-Makers in an Evolving Landscape
Our platform helps R&D, strategy, and BD teams track competitive shifts and mechanistic transitions across high-interest targets in I&I.
- Clinical teams receive structured comparators on trial design, development velocity, and outcome benchmarks across cytokine targets — enabling smarter design decisions.
- Portfolio strategists access historical transition patterns and saturation data to better time entry into maturing or consolidating mechanisms.
- Business development teams are supported with asset overlap and novelty analytics, clarifying whether an opportunity follows the curve — or leads it.
When the market moves from established to emerging targets, we help ensure you’re not just tracking the shift — but positioned ahead of it.
For more tailored, data-rich insights, let’s talk.



